https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Ogl4XnJb5es
This article was written due to the current state of our world right now. People are struggling to cope with stress due to uncertainty and worry because of job loss, lack of food, illness, loss of loved ones, and social isolation. Others are dealing with regular abuse as they are quarantined with their abuser and feel like they have no way out.
While hundreds of thousands worldwide have either battled the Coronavirus or have lost loved ones to the Virus, one thing I have noticed, and that is, liquor stores remain open as an essential service provider, at least in my area, and I am sure many others. There were reasons provided by the media regarding why they remained open. Some were valid and some were not (in my opinion).
This compelled me to educate some and remind others how excessive use of substances can cause a stressful situation to become worse. People are vulnerable when dealing with difficult circumstances – many times, turning to things that have the potential to be damaging if not deadly.
This article was written to inform readers on how excessive use of drugs and alcohol can cause Early Onset of Dementia. This condition is rarely talked about but without a fully functioning mind, life becomes even more difficult to manage especially during stressful times.
So, I hope many of you find this article useful and food for thought as you consider how to deal with difficult and stressful circumstances.
It is my hope that we all come out of this mentally stronger.
Okay, so here we go…..
When people hear of dementia, they generally think of an adult who is 65 years old or older. However, evidence shows that adults are now developing dementia in their late 30’s and early 40’s; and there are reasons for this (Chaston, 2010).
Let’s first start by defining what dementia is.
Dementia is a brain disease that is progressive disrupting how the brain functions. Dementia causes a decrease in memory, attention, understanding, balance, coordination, language, and judgment (much like the effects of drugs and alcohol). As dementia continues to progress, motivation, emotional regulation, and appropriate social behavior begin to deteriorate as well (Chaston, 2010).
Young or Early Onset Dementia, however, is a more aggressive dementia that devastates the lives of those suffering from it because it occurs during a time when careers are being established and children are still being raised. So, the individual begins to look for ways to cope with the decline in their mental and emotional status as well as deal with the impact that this condition has on their social and financial life (Chaston, 2010).
In many cases, young and middle-aged adults who have Early Onset Dementia are diagnosed with specific types – and that is – Vascular Dementia or Alcohol-Related Dementia.
So what is Vascular Dementia?
Vascular Dementia is the second most common form of dementia and is caused by a series of small strokes and other events that interfere with proper blood flow and oxygen to the brain. This damage stops the brain from functioning normally (National Institute of Health, [NIH], 2020).
Risk Factors related to Vascular Dementia.
There are many causes of Vascular Dementia. Some may be reversible, and some are not. Dementia that cannot be reversed is caused by injury or disease. Dementia that may be reversible is caused by the following (Arehart-Treichel, 2013; Chasten, 2010).:
- Alcohol
- Smoking
- Drugs
- Depression
- High blood pressure
- Heart disease
- Obesity
- Inactive Lifestyle
- Hormone or vitamin imbalances
- Thyroid disease
- Hydrocephalus
As you can see, the above-mentioned risk factors are either preventable or, if successfully managed, can decrease the risk of developing Vascular Dementia.
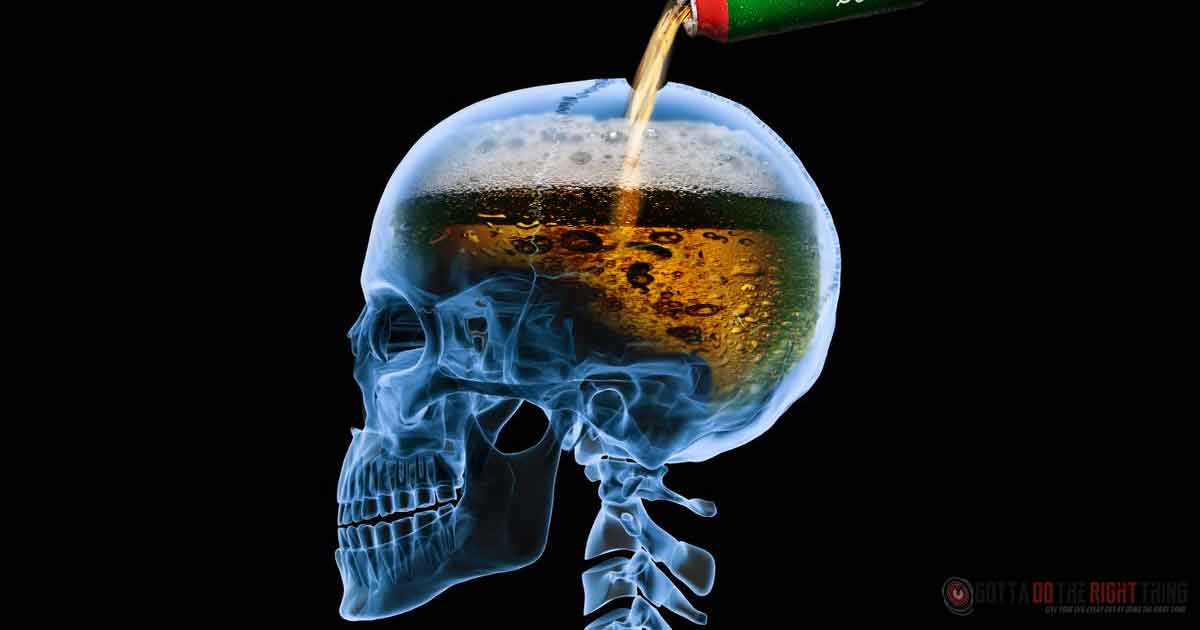
Alcohol-related brain damage or alcohol dementia
Alcohol-related brain damage (ARBD) also known as alcohol dementia is a brain disorder due to regular heavy drinking of alcohol over several years causing damage to the brain, and can also lead to addiction. (Alzheimer’s Society, 2020).
ABRD is a condition that causes a long-term decline in thinking and memory due to excessive alcohol use and the lack of vitamin B1. Vitamin B1 is required to provide the body with energy and is especially important for the brain and nerve cells because they use up so much energy to function properly (Alzheimer’s Society, 2020). Alcohol is a toxin so with regular heavy use, alcohol damages nerve cells, changes chemicals in the brain and causes the brain to shrink.
Drugs and alcohol use in teens and young adults
Although many risk factors can cause dementia, excess use of drugs and alcohol are known to be the main risk factors for an early-on-set of dementia (Arehart-Treichel, 2013). Therefore, regularly educating teens and young adults of these devastating long-term effects is imperative so that they at least know of the negative consequences and losses they may experience later on in life.
For many teens and young adults, drugs and alcohol are a go-to for “having fun”, partying, coping with anxiety, stress, acceptance, depression, purpose, boredom, trauma “escaping”, and pressure to succeed without having a clear direction on how actually do it (American Addiction Centers, 2020a).
Teen and young adult brain damage due to drugs and alcohol
https://youtu.be/zXjANz9r5F0
You see, by the time a child becomes a teen, most parts of the brain are developed to where a normal functioning teen’s memory is sharper than some adults; but there is still one important part of the brain that is not developed until the mid-twenties. Consequently, this puts the teen’s brain at a higher risk for the harmful impact that is caused by drug and alcohol use (Choices/Current Health, 2019).
During the teen years and into young adulthood, the area of the brain that is in charge of critical thinking and properly weighing out pros and cons before making a decision is still developing. Because this part of the brain is still developing, the teen/young adult automatically relies more on another part of the brain that is already developed to make decisions (Choices/Current Health, 2019).
What is more, the part of the brain that is already developed is linked to taking chances and risks, emotions, instant gratification and rewards instead of critical thinking. For example, A friend or someone the teen admires might pressure him/her to do something that they will later regret, but because the area of the brain that critically thinks about consequences and negative outcomes is not fully develop, the teen/young adult focuses on getting the reward, which in this case, is the friend/peers acceptance (Choices/Current Health, 2019).
Early drug and alcohol use also increases the risk of addiction because the brain of a young adult is very sensitive to dopamine; and addiction is closely associated with dopamine. When a drug is taken, it causes a rush of dopamine to go to the brain. This is the same feeling that occurs when someone experiences a rewarding activity. However with drugs, the rush of dopamine is much higher and intense and over time, the brain becomes used to the rush and looks for it (Choices/Current Health, 2019).
Heavy drinking and drug use in mid-life adults.
Current research shows that middle-aged adults who heavily drink, consuming more than 5 bottles of beer in one sitting or one bottle of wine, and/or use drugs, were three (3) times more likely than the general population to have dementia by the age of 65. Heavy drinking and drug use are both linked to stroke and dementia (Harding, 2015).
As stated, there are several sub-types of dementia that are linked to alcohol abuse. This is because alcohol and drugs kill the brain at a faster rate than age alone. (American Addiction Centers, 2020)
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=nSLzkLaOIvM
Changes in the brain
The brain is always looking for ways to gain new information to stay healthy and strong. As the brain continues to grow and takes in new knowledge, nerve cells continue to grow and strengthen pathways for new learning. These pathways are how the brain processes information supporting everything from the brain’s ability to learn, memorize, pay attention, have self-control, and feel emotions. However, if these nerve cells are not used, the brain gets rid of them (Choices/Current Health, 2019). With substance abuse, these pathways are not used as often due to the effects of the substance and therefore, the brain begins to rid the use of these functions while toxins are also are damaging the area of the brain responsible for producing these skills.
Worldwide problem
In doing this research, I came across a few countries that posted statistics regarding the early onset of dementia. This condition is widespread just like many other diseases and conditions.
Let’s take a look…
|
United States |
According to a 2004 survey from the Alzheimer’s Association, approximately 220,000-640,000 Americans are diagnosed with the early onset of dementia (Alzheimer’s Association, 2020). |
|
Asia |
In Asia, the early onset of dementia is a relatively new problem and yet accounts for one-third of all dementia cases seen at the National Neuroscience Institute (NNI); and still, YOD continues to increase in the Asian population. In 2015, NNI saw180 new cases. This is an increase of 100 new cases from the previous year (SingHealth, 2016). |
|
Australia |
Dementia is the second leading cause of death in Australia. In 2018, there were approximately 26,443 people with YOD. By 2025, early-onset dementia is expected to increase to 29,375 and further increase to 42,252 people by 2056 (Dementia Austrialia, 2018). |
|
New Zealand |
As of 2010, the International Research Community reports 2,243 young adults diagnosed with dementia (Chaston, 2010). |
|
United Kingdom |
There are an estimated 150,000 people with Vascular Dementia in the UK. 42,000 are living with Young Onset Dementia (Alzheimer’s Society, 2020a). |
Okay – so this is the scary part!
Diagnosis is often delayed until the symptoms of Early Onset Dementia are well established. Therefore, a timely diagnosis and treatment plan is delayed as well. A barrier to diagnosing dementia in younger adults are a failure on primary care’s part in recognizing the slow but growing symptoms (Bakker et al., 2013).
Good news!
In most cases, early onset of dementia can be prevented by lifestyle changes. Here are a few to consider (Chaston, 2010; Choices/Current Health, 2019; My Southern Health, 2019):
- Get regular exercise. This helps to increase blood flow to the brain. It also helps to naturally increase the dopamine levels in the brain.
- Learn something new. This helps to encourage new pathways and connections in the brain to strengthen and increase memory, attention, problem-solving, emotions, understanding, language, and good judgment intact.
- Participate in activities that require memory and paying attention.
- Make a habit of eating a healthy diet.
- Manage your weight and overall health.
- Manage your mental and emotional health and well-being. Stress, anxiety, depression, and worry contribute to a reduction in mental clarity, memory, and attention and can put the individual at risk for a relapse.
Get help for alcohol use disorder
Vascular or Alcohol Dementia is one of many problems linked with drug and excess use of alcohol. This condition is serious and can cause harm to many other organs in the body as well. Getting help from an addictions recovery center and rehabilitation is critical. It is the best way to overcome this persistent and chronic disease.
Medical professionals are available to help with the process of detoxing, understanding what triggers addiction, and how to change behaviors around-consuming drugs and alcohol. This will help the person to maintain a sober healthy life (American Addiction Centers, 2020).
Bottomline
This is not a mainstream topic and, therefore, is rarely talked about. However, the public needs to be aware of the potential long-term effects of excess or long-term use of drugs and alcohol. As we have learned, poor behavior and choices are more than just the effects of the actual drug and alcohol itself, but also could be a part of brain damage.
So now that you know, what will you do? The brain is resilient and many of the effects from drug and alcohol abuse, if caught early enough, can be prevented, or reversed (Chaston, 2010; Choices/Current Health, 2019).
Be your own advocate. Take care of yourself and live your best life as long as you can! ????
The Role of Occupational Therapy
Occupational Therapy specializes in prevention and health promotion focusing on physical, mental and behavioral issues that have contributed to beginning and continuing to use drugs and alcohol. Like all bad habits and addictions, it starts for one reason but continues for another reason (American Occupational Therapy Association, 2014).
When an individual has picked up a bad habit, it stops them from building a skill level to overcome life’s stressors in a positive way. Occupational Therapy works with each person by implementing a treatment plan that is customized to the individuals needs. We get to the root of the cause and assist with building life skills to help the individual maintain or regain their emotional, physical, and mental health and independence so that they can enjoy a quality life (American Occupational Therapy Association, 2014).
Additional Resources
SAMHSA’s National Helpline – 1-800-662-HELP (4357) substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration.
The NAMI HelpLine (National Alliance on Mental Health) can be reached Monday through Friday, 10 am–6 pm, ET. 1-800-950-NAMI (6264) or info@nami.org
National Domestic Violence Hotline – 800-799-7233
References
Alzheimer’s Association. (2020). Early onset dementia a national challenge, a future crisis. Alzheimer’s Association [PDF].
Alzheimer’s Society. (2020). Alcohol-related brain damage. Alzheimer’s Society.
Alzheimer’s Society. (2020a). What is young onset dementia. Alzheimer’s Society.
American Addiction Centers. (2020a). Teenagers and Drugs: 11 Real reasons Why Teenagers Experiment. American Addiction Centers.
American Addiction Centers. (2020). What are the links between alcohol and dementia. American Addiction Centers,
Arehart-Treichel, J. (2013). Early-Onset Dementia Linked To Alcohol Abuse, Other Factors. Psychiatric News, Sep 20, 2013, Vol.48(18), p.16,24
Bakker, C., De Vugt, M., Koopmans, R., Pijnenburg, Y., Van Vliet, D., Verhey, F. & Vernooij-Dassen, M., (2013). Time to diagnosis in young-onset dementia as compared with late-onset dementia. Psychological Medicine, 43(2), 423-432. doi:10.1017/S0033291712001122
Chaston, D. (2010). Younger adults with dementia: A strategy to promote awareness and transform perceptions, Contemporary Nurse, 34:2, 221-229, DOI: 10.5172/conu.2010.34.2.221
Choices/Current Health. (2019). Drugs and the teen brain: Adolescence is a critical time in brain development. That means teens are at greater risk of experiencing the harmful effects of drugs and alcohol. Choices/Current Health, 34(4), 14+. Retrieved from https://link-gale-com.ezproxy.philau.edu/ apps/doc/A567634044/BIC?u=phil37611&sid=BIC&xid=2ade53be
Dementia Austrialia. (2018). Dementia key facts and statistics. Dementia Australia.
Harding, A. (2015). 8 dementia risk factors. Everyday Health.
My Southern Health. (2019). How to reduce your risk of developing Alzheimer’s or another form of dementia. Vanderbilt Health.
SingHealth. (2016). Young Onset Dementia (YOD): Dementia May Affect Younger People Too. Head & back: Brain and nervous system. Health Xchange.sg.


Like!! Thank you for publishing this awesome article.
You are very welcome. This is a topic that is rarely spoken about that I thought needed the public’s attention so that better choices can be made if you choose. Take Care! 🙂
An impressive share! I have just forwarded this onto a coworker who was conducting a little research on this.
And he in fact ordered me dinner due to the fact that I
found it for him… lol. So let me reword
this…. Thanks for the meal!! But yeah, thanks for spending some time to talk about this issue here on your website.
Have a look at my web blog – buy CBD
You are very welcome. This is a topic that is not talked about too much, but it is so important for the public to know that certain lifestyle choices can lead to early dementia so the public can make better or different choices if they so choose. Thank you for your feedback. Take care! 🙂
It’s amazing designed for me to have a site, which is useful in support
of my knowledge. thanks admin
Look at my homepage Bernadette
You are very welcome. I’m glad that you find this site to be helpful 🙂